Odoo 19 markiert einen bedeutenden Wendepunkt in der Art und Weise, wie Künstliche Intelligenz in die Plattform integriert wird.
Statt KI lediglich als nachträgliches Add-on zu betrachten, hat Odoo sie durch native Vektordarstellungen (Embeddings), RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) und konfigurierbare KI-Agenten direkt in das Herzstück des Frameworks eingewebt.
Doch wie funktioniert das Ganze genau? Welche Versprechen kann die Technologie wirklich einlösen? Und wie lässt sie sich anpassen oder erweitern?
WWir haben den Quellcode analysiert, um die Fragen zu beantworten, die Odoo-Experten heute bewegen.
Erfahren Sie alles über die Logik der KI-Architektur von Odoo 19, was Sie anpassen können und welche Bereiche noch Neuland sind.
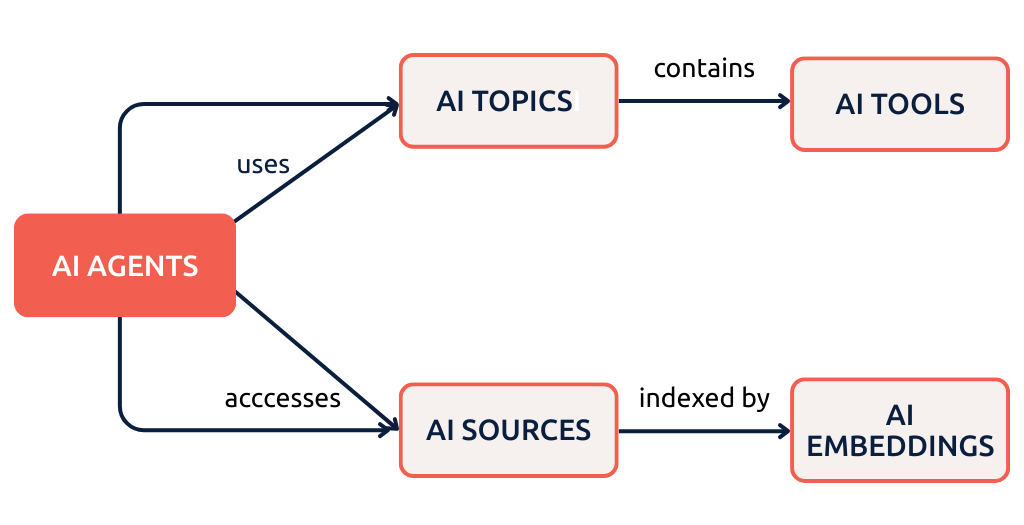
Die 3 Säulen der Odoo KI-Architektur
Die KI-Funktionalität von Odoo 19 basiert auf drei zentralen Elementen:
- Vektordatenbank für RAG: Embedding-basierte Dokumentensuche, um KI-Antworten auf Basis Ihrer eigenen Daten zu validieren.
- KI-Agenten: Konfigurierbare Assistenten, die Systemanweisungen (Prompts), Themenbereiche, Werkzeuge und Datenquellen bündeln.
- KI-Tools: Server-Aktionen, die dem Sprachmodell (LLM) zur Verfügung gestellt werden, um direkt mit Odoo-Daten zu interagieren.
Vektor-basiertes RAG
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) sorgt dafür, dass die KI relevante Informationen in Ihren Dokumenten findet, bevor sie antwortet.
Statt bei jeder Anfrage alles zu lesen, wandelt Odoo Ihre Dokumente in mathematische Muster (Vektoren) um.
Bei einer Anfrage werden blitzschnell die passenden Abschnitte identifiziert und der KI als Kontext mitgegeben.
So zitiert das System präzise aus Ihren Richtlinien, statt Fakten zu erfinden.
Odoo KI-Agenten
Ein KI-Agent ist ein virtueller Assistent in Ihrem Odoo.
Er kann Fragen beantworten, Aufgaben steuern oder Informationen aus Ihren Dokumenten extrahieren.
Er fungiert wie ein ChatGPT, das Ihr Unternehmen in- und auswendig kennt: Er prüft Verkaufszahlen, entwirft E-Mails oder erklärt interne Abläufe.
Odoo KI-Tools
KI-Tools sind die Schnittstellen zur Aktion.
Wenn Sie fragen: „Zeig mir meine offenen Angebote“, nutzt der Agent ein Tool für eine direkte Datenbankabfrage.
Diese Tools erlauben es der KI, Datensätze zu erstellen oder Berichte abzurufen, statt nur Texte zu generieren.
Wichtig: Odoo setzt zwingend PostgreSQL mit der pgvector-Erweiterung voraus. Ohne dieses Modul ist keine Vektorsuche möglich. Dies ist eine der entscheidenden neuen Systemvoraussetzungen für Odoo 19.
Schauen wir uns die technischen Details Schritt für Schritt an.
Wichtig: Odoo setzt zwingend PostgreSQL mit der pgvector-Erweiterung voraus. Ohne dieses Modul ist keine Vektorsuche möglich. Dies ist eine der entscheidenden neuen Systemvoraussetzungen für Odoo 19.
Schauen wir uns die technischen Details Schritt für Schritt an.
1. Der Odoo-Vektorspeicher baut Ihre KI-Datenbank
RAG (“Retrieval-Augmented Generation”) ist ein Architekturmuster, das es der KI ermöglicht, Ihre Inhalte nativer und schneller zu erfassen, um die Antworten des Modells mit echtem Wissen zu ergänzen. Es wird manchmal als „KI-Datenbank“ bezeichnet, ist im Grunde aber ein Vektorspeicher innerhalb von PostgreSQL.
In Odoo 19 basiert das RAG-System auf dem Modell ai.embedding. Dieses Modell bezieht Daten aktuell ausschließlich aus den Quellen (ai.agent.source), die mit einem Agenten (ai.agent) verknüpft sind.
Derzeit scheint es kein Limit für die Anzahl der Quellen pro Agent zu geben.
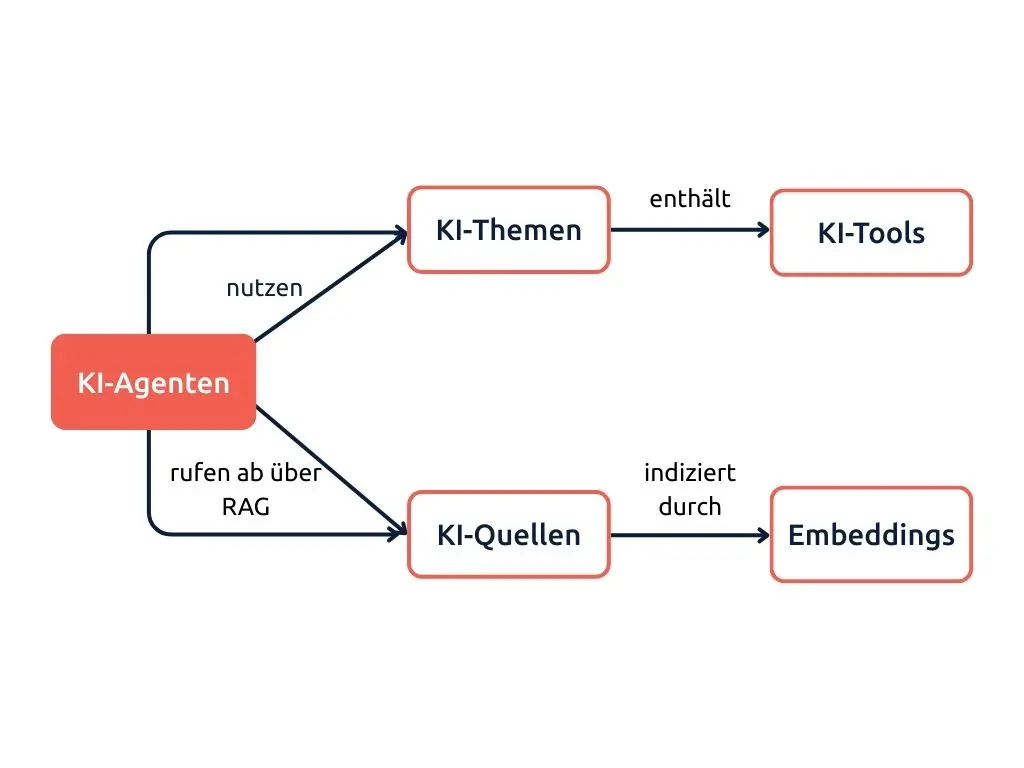
Das passiert, wenn Sie eine Quelle zu einem KI-Agenten hinzufügen:
Odoo KI-Agent-Pipeline
- Source addition: Wenn Sie einen Knowledge-Artikel, ein PDF oder eine andere Quelle zu einem KI-Agenten hinzufügen, wird ein Datensatz im Modell ai.agent.source erstellt.
- Cron-Trigger: Zwei geplante Aktionen werden aktiv: AI Agent Sources: Process Sources und AI Embedding: Generate Embeddings.
- Textextraktion: Der Inhalt der Quelle wird extrahiert und in verarbeitbare Abschnitte (Chunks) unterteilt.
- API-Aufruf: Jeder Abschnitt wird an den konfigurierten LLM-Anbieter (OpenAI oder Google) gesendet, um über ein Basis-Embedding-Modell die Vektoren zu berechnen.
- Speichern: Die Vektoren werden in der Tabelle ai.embedding unter Verwendung des nativen vector-Datentyps von pgvector abgelegt.
Der Status der Quelle wechselt von Processing zu Indexed, sobald die Embeddings abgeschlossen sind. Updates werden automatisch durch die Cron-Jobs verarbeitet.
FAQs zum Odoo-Vektorspeicher
Wo sind die Vektoren in Odoo hinterlegt?
Vektoren werden immer zentral im Modell ai.embedding gespeichert – niemals direkt im Quelldatensatz selbst.
Dieser Ansatz gewährleistet eine effiziente Ähnlichkeitssuche über alle indizierten Inhalte hinweg.
Können diese Vektoren in anderen Modellen oder Datensätzen verwendet werden?
Wenn Sie ir.model.fields für das Feld embedding_vector prüfen, werden Sie feststellen, dass der Feldtyp (ttype) leer (null) ist. Das ist kein Bug, sondern eine Folge der Implementierung des pgvector-Supports.
Odoo hat den neuen Feldtyp Vector eingeführt, der direkt mit der pgvector-Erweiterung kommuniziert, diesen aber nie zum Auswahlfeld ttype in ir.model.fields hinzugefügt.
Ob dies Absicht oder ein Versäumnis war, ist unklar – auf Datenbankebene funktioniert das Feld jedenfalls korrekt.
Es erschwert jedoch die Übertragung auf andere Modelle, da bisher auch kein Mixin verfügbar ist.
Welche Daten werden von Odoo wirklich vektorisiert (embedded)?
Bei der Nutzung der neuen KI-Features fühlt es sich so an, als würde die Suche in Produkten oder Verkaufschancen hervorragend funktionieren.
Aber: Odoo nutzt derzeit keine Embeddings für Standardmodelle wie Leads, Produkte oder Kontakte. Die beeindruckenden Suchfähigkeiten der Agenten stammen von Tools, nicht von Embeddings.
Fragen Sie die KI: „Zeig mir meine offenen Chancen“, führt sie keine semantische Vektorsuche aus, sondern ruft ein Tool auf, das eine Standard-Datenbankabfrage ausführt.
Da dies effizienter, günstiger und schneller ist, erwarten wir, dass Odoo die Tools weiter verbessert, statt alle Daten in ein RAG zu zwingen.
Aktuell fließen nur Inhalte aus ai.agent.source (Knowledge, PDFs, Dokument-Uploads, Links) in das RAG ein.
Die Art, wie die Modelle aufgeteilt sind, ermöglicht es Odoo und uns jedoch, später weitere Daten zu unserem lokalen RAG hinzuzufügen.
Wie wird die KI-Vektorsuche in Odoo in Zukunft wohl weiterentwickelt?
Die besten Kandidaten für die Odoo-Vektordatenbank sind unserer Meinung nach Elemente, die bereits nah an den Agent-Quellen liegen:
- Alle Artikel der Knowledge-App
- Sämtliche Dokumente
Das würde es ermöglichen, Duplikate effizient zu identifizieren und dem Nutzer proaktiv verwandte Quellen vorzuschlagen – was Agenten bereits im Standard extrem leistungsfähig machen würde.
Ein weiterer, weniger offensichtlicher Schritt wäre die Einbindung von Modellen mit hohem Textanteil. Dies würde fortschrittliche, semantische Suchfunktionen für folgende Bereiche ermöglichen:
- Projekt-Aufgaben: Erkennung ähnlicher Tickets und automatisches Verfassen von Aufgaben basierend auf der Historie.
- Helpdesk: Automatische Erstellung von FAQs in der Knowledge-App sowie KI-gestützte Antworten auf Basis früherer Lösungen.
- Produkte: Intelligentes Matching von Produkten basierend auf detaillierten Beschreibungen.
- Jeder andere Prozess, der auf umfangreichen Textdaten basiert.
Wir hoffen, dass Embeddings in Odoo 20 kosteneffizienter und pgvector noch schneller wird.
Tatsächlich implementieren wir bei much. Consulting bereits eigene RAG-Lösungen für genau diese Odoo-Modelle.
Unser Fazit bisher? Die Anwendungsmöglichkeiten, die sich daraus ergeben, sind beeindruckend.
2. KI-Agenten erstellen Antworten über eine Prompt-Sequenz
Wenn ein Benutzer eine Prompt an einen KI-Agenten sendet, erstellt Odoo die Anfrage in einer bestimmten Reihenfolge:
So setzt Odoo KI-Anfragen zusammen
1. System-Prompt
Die Odoos Basis-Prompts bilden das Fundament. Das sind detaillierte Systemanweisungen für das LLM. Zusätzlich werden hier alle Tool-Prompts ebenfalls hinzugefügt.
2. Agent-Prompt
Die spezifischen Anweisungen für den jeweiligen Agenten werden ergänzt.
3. Kontext-Anreicherung
Objekt-Kontext: Das aktuelle Datum und Benutzerinfos werden angehängt. Bei Anfragen aus einem Datensatz fließen dessen Informationen ebenfalls ein.
RAG-Kontext: Relevante Textabschnitte aus den Quellen des Agenten werden per Ähnlichkeitssuche abgerufen und der Nachricht beigefügt.
4. Benutzernachricht
Die Eingabe des Benutzers wird beigefügt.
5. API-Aufruf
Die vollständige Anfrage wird an das LLM (OpenAI oder Google) gesendet.
6. Tool-Ausführung
Entscheidet sich die KI für ein Tool, führt Odoo dieses aus und speist das Ergebnis zurück. Dieser Vorgang kann sich mehrfach wiederholen.
7. Finale Antwort
ie KI generiert ihre Antwort basierend auf dem gesamten Kontext.
Dieser Prozess-Loop kann sich mehrfach wiederholen, falls die KI mehrere Tools aufrufen muss, um Informationen zu sammeln, bevor sie antwortet.
Interessanterweise gibt Odoo dabei einige Limits vor, die über die Systemparameter angepasst werden können:
- ai.max_successive_calls (Standard 20): Erlaubt bis zu 20 aufeinanderfolgende Aufrufe an den Agenten, falls keine sofortige Antwort gefunden wird. Das verbraucht bei realen Workloads viele Token.
- ai.max_tool_calls_per_call: Das LLM darf Tools nur maximal 20 Mal pro Durchgang aufrufen, um extrem lange Ladezeiten und eine zu hohe Datenbanklast zu vermeiden.
3. Agenten interagieren über Themen (ai.topic) und Tools mit Odoo-Daten
KI-Tools sind in Odoo hinterlegte Server-Aktionen (ir.actions.server). Die Brücke zwischen dem KI-Agenten und diesen Aktionen schlägt das Modell Themen (ai.topic). Ein Thema fungiert als Container, der eine Gruppe von Server-Aktionen bündelt und sie für die KI beschreibt.
Wie funktionieren KI-Tools technisch?
Jedes Thema (ai.topic) verfügt über ein Many2many-Feld, das auf bestehende Server-Aktionen verweist.
Sobald Sie eine Server-Aktion in ein Thema aufnehmen und dieses Thema einem Agenten zuweisen, kann die KI diese Aktion als „Tool“ nutzen:
Sichtbarkeit für das LLM: Odoo übergibt die Beschreibung der Server-Aktion an die KI. So weiß der Agent, wofür das Tool gut ist (z. B. „Erstelle einen Lead“ oder „Suche Produkte“).
Interaktion: Die KI entscheidet selbstständig, wann sie welches Tool benötigt. Sie ruft dann die Server-Aktion mit den entsprechenden Parametern auf.
Vorteil: Da Tools auf Standard-Server-Aktionen basieren, können sie alles, was Odoo auch sonst kann:
- Details zu Feldern in Odoo-Modellen abrufen
- Verschiedene Ansichten öffnen (Formular, Liste, Pivot, Grafik)
- Datensätze erstellen (Leads, Aufgaben usw.)
- Daten zu suchen und abzurufen
- Benutzerdefinierte Geschäftslogik ausführen.
Wichtig: Wenn die KI Ihr CRM durchsucht oder Produktdaten abruft, ruft sie Tools (Server-Aktionen) auf, die Standard-Datenbankoperationen ausführen.
Hierfür werden keine Embeddings genutzt.
Es handelt sich um reguläres Odoo-Querying, nicht um semantische Suche.
Kann man eigene KI-Tools für Odoo erstellen?
Ja, und hier ist der sauberste Weg, um Agenten zu erweitern, ohne den Core-Code anzupassen:
- Server-Aktion erstellen: Programmieren Sie eine neue Server-Aktion mit Ihrer individuellen Python-Logik.
- Thema (ai.topic) konfigurieren: Erstellen oder wählen Sie ein passendes Thema aus.
- Verknüpfung: Fügen Sie Ihre Server-Aktion dem Many2many-Feld „AI Tools“ des Themas hinzu.
- Zuweisung: Verknüpfen Sie das Thema mit Ihrem Agenten.
Dadurch wird jede beliebige Odoo-Funktionalität sofort für Ihre KI-Agenten nutzbar.
Odoo KI anpassen: Möglichkeiten und Grenzen
Hier ist eine praktische Übersicht, wie Sie Odoo KI an Ihre Bedürfnisse anpassen können: von Zero-Code-Lösungen bis hin zu tiefergehenden Entwicklungen und Zukunftsaussichten.
Einfach ohne Programmierung anpassbar:
- System-Prompts: Sie haben die volle Kontrolle über die Persönlichkeit des Agenten und seine grundlegenden Instruktionen.
- Quellen: Fügen Sie beliebig viele Knowledge-Artikel oder externe Dokumente hinzu.
- Themen (Topics): Erstellen Sie neue Themen und verknüpfen Sie diese flexibel mit Ihren Agenten.
- Neue einfache KI-Tools: Erstellen Sie einfache Server-Aktionen und geben Sie diese als Werkzeuge für die KI frei.
- Antwort-Stil: Konfigurieren Sie direkt, wie der Agent mit dem Benutzer kommunizieren soll.
Möglich, erfordert aber Entwicklungsaufwand:
- Basis-URL für KI-Anbieter: Diese kann über Systemparameter oder spezifische Einstellungen angepasst werden.
- Neue, komplexe KI-Tools: Durch das Programmieren individueller Server-Aktionen und deren Verknüpfung mit Themen lassen sich auch komplexe Workflows abbilden.
Derzeit noch eingeschränkt:
- RAG für eigene Modelle: Odoo indiziert standardmäßig keine benutzerdefinierten Modelle oder Stammdaten; hier wäre erheblicher Aufwand nötig, um eine eigene Embedding-Logik nachzurüsten.
- Hardcodierte Endpunkte: Da die individuellen API-Endpunkte (nicht nur die Basis-URL) fest im Code hinterlegt zu sein scheinen, ist ein „Drop-in“-Ersatz durch selbstgehostete LLMs aktuell ungewiss.
- Chatter-Aktionsbuttons: Die Buttons „Als Nachricht senden“ und „Als Notiz schreiben“ sind derzeit fest im JavaScript-Frontend kodiert.
Odoo
-API-Endpunkte – fest hinterlegt oder konfigurierbar?
Das ist eine entscheidende Frage für Unternehmen, die selbstgehostete LLMs, LLM-Aggregatoren oder KI-Dienste über Cloud-Provider (wie AWS Bedrock, Azure OpenAI oder Vertex AI) nutzen möchten.
So sieht die aktuelle Lage in Odoo aus:
- Die Basis-URL lässt sich ändern.
- Die einzelnen API-Endpunkte sind jedoch im Code hartcodiert.
- Diese Endpunkte sind spezifisch auf die API-Strukturen von OpenAI und Google zugeschnitten. Sie funktionieren also nur dann reibungslos, wenn der alternative Dienst exakt dieselben Endpunkt-Strukturen implementiert.
Das bedeutet: Sie können zwar auf eine andere URL verweisen, aber es ist unsicher, ob ein selbstgehostetes LLM mit einer abweichenden API-Struktur ohne Weiteres funktioniert.
Das LLM müsste entweder Odoo-kompatible Endpunkte simulieren, oder es wäre ein erheblicher Anpassungsaufwand im Odoo-Core nötig.
Wir erwarten jedoch, dass bald zahlreiche Marketplace- oder OCA-Lösungen erscheinen werden, die weitere Modelle und Dienste nativ anbinden.
Tipps für die Praxis
Für Implementierer
Erwarten Sie keine semantische Suche bei Leads oder Produkten: Das läuft über Tools und Datenbankabfragen, nicht über RAG.
Investieren Sie in gute Knowledge-App-Artikel: Das ist der beste Content für Ihre KI-Agenten, weil Sie das Wissen dort jederzeit einfach aktualisieren können.
Eigene Tools sind Ihr bester Freund: Sie sind der sauberste Weg, um die Fähigkeiten Ihres Agenten zu erweitern.
Testen Sie mit echten Daten: Die Qualität von RAG steht und fällt mit der Qualität Ihren Quellen.
Für Entwickler
Der Feldtyp „Vector“ funktioniert: Lassen Sie sich nicht vom null-Wert bei ttype irritieren, in der Datenbank läuft alles wie geschmiert.
pgvector ist Pflicht: Ihr PostgreSQL-Setup muss diese Erweiterung unbedingt enthalten.
Server-Aktionen sind der Dreh- und Angelpunkt: Bauen SIe Tools über Server-Aktionen auf, anstatt den Core zu modifizieren.
JavaScript für UI-Änderungen: Wenn Sie die Aktions-Buttons anpassen wollen, müssen Sie ans Frontend ran.
Die Zukunft von KI in Odoo
Oie KI-Architektur von Odoo 19 ist ein super Fundament, aber ganz klar erst der Anfang.
Wir rechnen damit, dass künftige Versionen die RAG-Fähigkeiten auf weitere Modelle ausweiten, mehr eingebaute Tools mitbringen und die Flexibilität bei den KI-Anbietern verbessern.
Vorerst arbeitet das System innerhalb seines Rahmens hervorragend: dokumentenbasiertes RAG kombiniert mit toolbasierten Odoo-Interaktionen.
Wenn man diese Mechanismen versteht, hilft das extrem dabei, realistische Erwartungen zu setzen und genau zu wissen, wo sich Anpassungen wirklich lohnen.
Sprechen wir über IHR Odoo KI-Setup!
Unsere Experten arbeiten bereits intensiv mit Kunden an KI-gestützten Odoo-Projekten.
Wir freuen uns darauf, unsere Erfahrungen mit Ihnen zu teilen und Lösungen auf Ihre Bedürfnisse zuzuschneiden.